Hire Dedicated Virtual Assistants Managed Just for You
Hire skilled VAs to streamline your tasks and achieve more every day. Get started in just 24 hours to save up to 50% on operational cost. Transform your operations while cutting costs significantly.
Have us worry about the FULFILMENT while you focus on scaling.
What We Specialize in

Standalone Virtual Assistants
Our standalone virtual assistants are here to help you stay organized, manage workflows, and get things done, without the hassle.

Complete White-Label Fulfillment Team
Our white-label fulfillment team handles all your backend operations, from GHL setup, marketing, and development, without your clients ever knowing.

Done-For-You Marketing Service
We handle your marketing from start to finish, so you can focus on growing your business. Simple, effective, and stress-free.
Fuel Your Growth with Industry-Savvy, Affordable Virtual Assistants.
Perfectly Suited For
01
Digital Marketing Agency Owners
Maximize ROI with tailored marketing support.
02
Social Media Marketing Agency Owners
Scale campaigns efficiently with expert assistance.
03
Local Businesses
Increase local reach and customer engagement.
04
SaaS Businesses
Optimize operations and accelerate SaaS growth.
Gohigh Level Certified Admins

Your Secret Weapon for GoHighLevel Success!
We’re the only Company dedicated solely to GoHighLevel CRM mastery—offering certified experts, hands-on support, and onboarding specialists to turn your CRM into a growth engine.




Industry's Most In-Demand Experts all at just $5/hour

GHL Experts
Our GoHighLevel experts optimize CRM workflows, build high-converting funnels, and automate your business. They’ll streamline your processes and help you achieve real results quickly and efficiently.

AI Bot Developers
Specializing in AI-powered systems, our developers create intelligent bots, automate workflows, and integrate tools like GoHighLevel and Zoho—providing smarter solutions to improve your efficiency.

No-Code Developers
Our no-code developers build powerful solutions without writing a single line of code. Whether it's apps, automations, or custom workflows, we bring your ideas to life faster and without the coding hassle.

WordPress Developers
Our WordPress developers create custom websites, optimize performance, and ensure seamless user experiences. From landing pages to full-scale sites, we’ll bring your vision to life with precision and speed.

N8N Experts
Our N8N experts specialize in automation, integrating tools and systems to streamline your workflows. Whether it’s integrating CRMs, marketing platforms, or custom processes, we’ll help you automate your business operations effortlessly.

Account Managers
Perfect for SaaS agency owners, our account managers handle onboarding, client success, and team coordination. They ensure smooth operations while you focus on growing your business.

Video Editors
Our video editors create high-quality edits for your brand, social media, and ads. Using AI-powered tools, we ensure your content stands out and connects with your audience.

Graphic Designers
From landing pages to social media visuals, our graphic designers elevate your brand with stunning designs that capture attention and engage your audience.

Media Buyers
With years of experience, our media buyers craft result-driven campaigns to maximize your ad performance and ROI, making sure every dollar spent delivers value.

Project Managers
Our project managers ensure the smooth execution of your projects, keeping everything on track so you can focus on scaling your business and reaching your goals.

SEO/AEO Experts
Boost your online visibility and drive traffic with our SEO/AEO specialists. Using proven strategies, they’ll optimize your site to achieve fast, sustainable results for your business.

Content Writers
From blogs to web copy, our content writers craft SEO-optimized content that tells your brand’s story and connects with your target audience.

Appointment Setters
Our appointment setters manage your calendar and bookings, ensuring you never miss an opportunity to connect with prospects or clients.

Admin/Inbox Management VAs
Our admin VAs handle your emails, calendar, and tasks, so you can stay organized and focus on growing your business.

Data Analysts
Our data analysts dive deep into your business data, providing actionable insights and reports. With a keen eye for trends, they’ll help you make data-driven decisions to optimize your strategy and boost growth.
Need Assistance? Contact Rozi Academy Now!
Get Matched with Your Perfect VA Fast

Discover Call
Schedule a quick call to explore your needs and understand how we can help you scale with the right support.


Onboarding with
Necessary Details
Once you’re ready, we’ll guide you through a seamless onboarding process, collecting all the necessary details to match you with the perfect assistant.


Fast Placement with VA
We’ll place a skilled virtual assistant that fits your business needs, ready to support your growth and streamline your operations.
Freelancers
Limited to Scope-Defined Projects: Often restrictive and inflexible.
Communication Gaps: Prone to delays and miscommunication.
Short-Term Commitment: Freelancers aren’t always invested in long-term success.
Higher Costs for Quality: Quality freelance work can cost $6K+.
Virtual Assistant vs. Freelancer: Discover the difference with a dedicated team.
VS
Rozi Academy
Branded, Multi-Platform Support: Our virtual assistants represent your brand across every channel.
Dedicated Team for You and Your Clients: A full-service team committed to your agency’s success.
Elite-Level Communication: Dedicated Slack channels for seamless, on-demand support.
Aligned with Your Goals: Tailored to your brand and business objectives.
Consistent, Reliable Service: Professionalism and accountability at every step.
100+ Ready-to-Use Automations: Snapshots, SOPs, and integrations included.
Predictable Flat-Rate Pricing: Enjoy unlimited funnels, automations, AI, and integrations—no surprises.
Our Partners
We are proud to collaborate with a diverse group of trusted partners who share our vision for innovation, quality, and growth. These partnerships enable us to deliver exceptional value, expand our capabilities, and create meaningful impact across industries. Each partner plays a crucial role in supporting our mission and helping us exceed client expectations. Together, we drive progress, inspire solutions, and build a stronger future.

Effortlessly Manage Your Workload with Our Virtual Assistants
Choosing virtual assistants shouldn’t feel hard. We make it easy. With our professional virtual assistants, we help you streamline your processes, ease your workload, and scale your business—all with the expertise of our dedicated team.
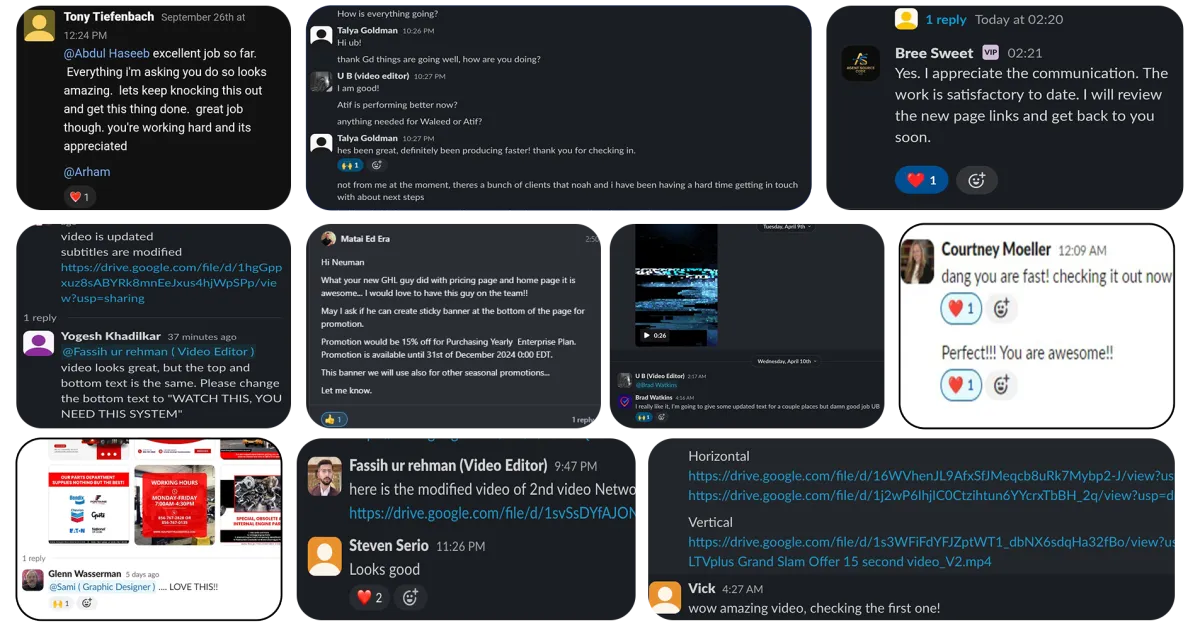
Stop Settling for Random VAs – Experience the Power of Our Managed VAs
Choosing virtual assistants shouldn’t feel hard. We make it easy for you. When you work with us you receive the help of both a professional virtual assistant plus our team’s full expertise for optimized performance.

Elite, Handpicked Talent
Every virtual assistant is carefully selected and trained to drive your business forward, supported by a dedicated project manager.
Work on Your Schedule
Your VA operates in your time zone, with live time tracking so you always know what’s happening, as it happens.
Trend-Ready & Always Improving
Regular brainstorming and trend updates keep our VAS sharp and ready to bring fresh ideas to your business.
Daily Check-Ins, Real Results
Stay in the loop with daily updates on progress and next steps, so you know exactly what’s being achieved and what’s next.
Our Testimonials
Get in Touch With Us
Our services are available 24/7
Book An Appointment
Frequently Asked Questions
Choosing virtual assistants shouldn’t feel hard. We make it easy for you. When you work with us you receive the help of both a professional virtual assistant plus our team’s full expertise for optimized performance.
What makes Rozi Academy’s virtual assistant services different from freelancers?
Rozi Academy offers a fully managed team of affordable virtual assistants, including personal virtual assistants, customer service virtual assistants, and even lead generator virtual assistants. Unlike freelancers, our virtual assistants are backed by an entire team for consistent reliability, support, and professionalism. Whether you’re looking for the best virtual assistant services or virtual assistant packages, we provide tailored solutions to suit your needs.
What types of services do your virtual assistants offer?
Our list of virtual assistant services is extensive and includes CRM virtual assistants, ecommerce virtual assistant services, marketing virtual assistant services, and virtual assistant SEO services. We also offer personal assistant services and virtual administrative assistant services to handle everything from client support to complex project management, making us one of the top-rated virtual assistant companies.
How do your affordable virtual assistant services help with business growth?
Our affordable virtual assistant services are designed to scale with your business, covering everything from lead generation and customer service to virtual administrative services. We focus on providing high-impact support through a dedicated, highly trained team, enabling you to focus on growth. We are one of the top virtual assistant companies known for our commitment to quality and cost-effectiveness.
What is included in your virtual assistant service packages?
Each virtual assistant service package is tailored to client needs and may include virtual executive assistant services, CRM management, SEO, marketing, and more. Our flexible pricing for virtual assistant services makes it easy for businesses to choose a package that best suits their requirements, with options for both one-time and ongoing support.
How are your virtual assistants trained for specific tasks like SEO and customer service?
Our virtual assistants undergo extensive training in specialized areas, such as virtual assistant SEO services, customer service, and ecommerce support. With our skilled team, you’ll have access to the most in-demand virtual assistant services, from marketing to administrative assistance, ensuring high-quality performance in every task.
Are your virtual assistant services available for businesses in the UK?
Yes, Rozi Academy provides virtual assistant services in the UK and worldwide. Whether you’re looking to hire a virtual assistant in the UK or need a PA recruitment agency in London, our services are available to support your unique needs. We work with clients across various regions, providing virtual administrative services, personal assistant services, and more, with tailored support for UK businesses.
Check out our Learning Resources Center

Creating Brand Guidelines: The Ultimate Guide for Businesses
Businesses establish the basis for their brand’s identity and consistency when creating brand guidelines. Such guidelines make sure that a…

Email Marketing Best Practices for Business Growth
Introduction Email marketing is still one of the most effective tools for SaaS founders, agency owners, and digital marketers. Global…

Product Page Optimization: A Key to Boosting Conversions
In the high-paced world of e-commerce, optimization of product pages is essential for sales growth and user experience improvement. Whether…

How GHL Real Estate Automation Helped a Real Estate Agency Close 40% More Deals
Discover how GHL Real Estate CRM helped one agency close 40% more deals in 60 days, built & managed by Rozi Academy's certified GoHighLevel team ...more
GHL CRM
March 05, 2026•12 min read

GoHighLevel CRM Platform: Automation & Growth Tech
Learn how GoHighLevel CRM combines automation, intelligent workflows, and reputation management tools to power next-level business technology. ...more
GHL VA Services
March 03, 2026•9 min read

GHL VA Services: Streamline Your Business with Certified GoHighLevel Experts
Discover how Rozi Academy’s GHL VA services help businesses automate workflows, reduce costs, and scale efficiently with certified GoHighLevel experts. Book a Discovery Call today! ...more
GHL VA Services
March 02, 2026•9 min read

Being a leading virtual assistant company, RoziAcademy offer you with a proactive, tech-savvy, self-starter virtual assistants across a range of sectors.
Resources
Contact Us
30 Riverhead Close, London, England, E17 5PY
312 SW GREENWICH DR LEES SUMMIT, MO 64082
UAE: 056 208 9979
USA: 816 219 8853
UK: 746 067 9604
Copyright 2026. Rozi Academy . All Rights Reserved.

















